
Table of Contents
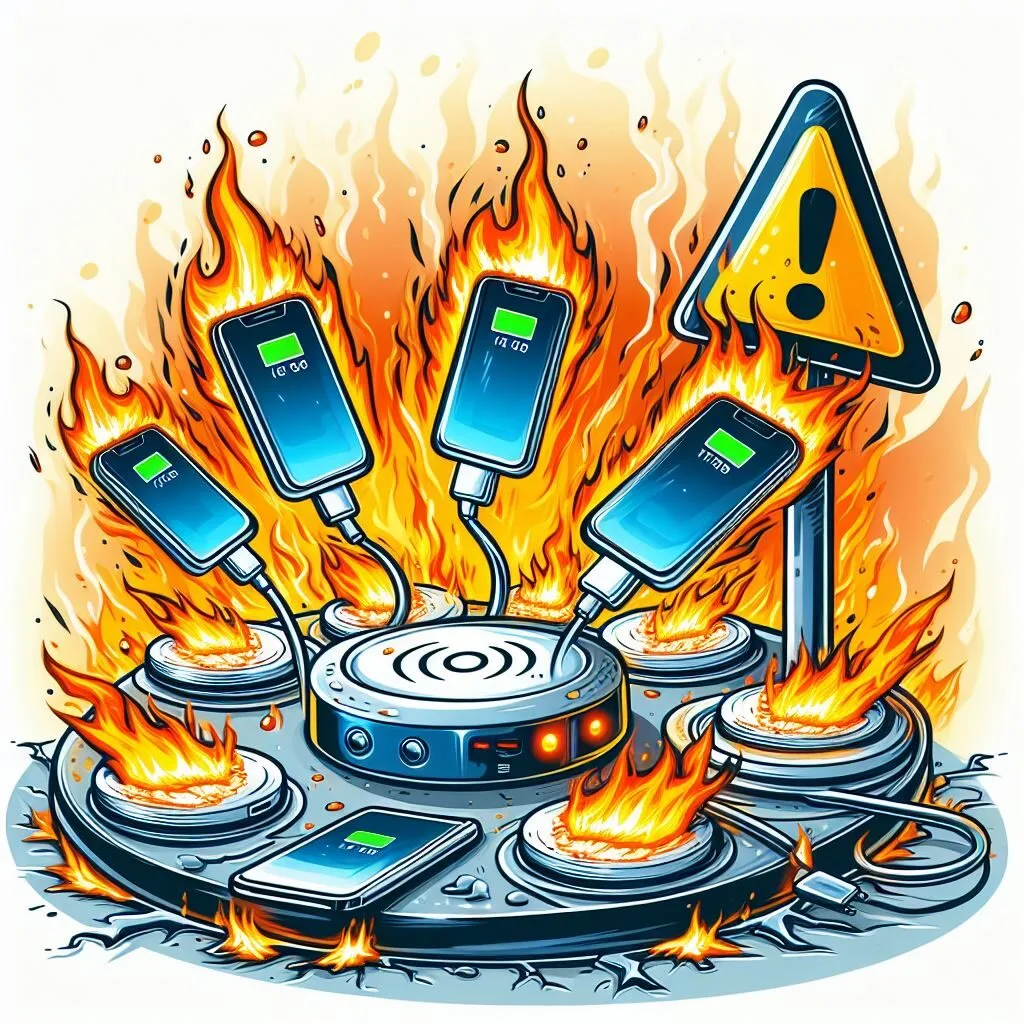
In the fast-paced world of technology, innovation is accompanied by new vulnerabilities. One such emerging threat is the VoltSchemer attack, a sophisticated exploit that targets wireless chargers to inject malicious voice commands and potentially fry devices.
Understanding its modus operandi and implementing effective countermeasures is crucial to safeguarding against this evolving threat landscape.
Introduction to VoltSchemer Attacks
VoltSchemer attacks represent a novel approach to exploiting wireless charging technology, which has become increasingly prevalent in modern devices such as smartphones, smartwatches, and other IoT devices. While wireless charging offers convenience and simplicity, it also introduces new attack vectors that malicious actors can exploit.
The term “VoltSchemer” originates from the combination of “volt,” referencing electricity, and “schemer,” indicating a devious or malicious actor. These attacks aim to compromise the integrity of devices by exploiting vulnerabilities in wireless charging protocols and firmware.
Modus Operandi of VoltSchemer Attacks
1. Exploiting Wireless Charging Protocols
VoltSchemer attacks typically begin with the exploitation of vulnerabilities within wireless charging protocols. Malicious actors reverse-engineer these protocols to identify weaknesses that can be exploited to execute their attack. By understanding the communication protocols used between the charging pad and the device, attackers can inject malicious commands.
2. Injecting Malicious Voice Commands
Once vulnerabilities are identified, attackers can leverage them to inject malicious voice commands into the device. This is particularly concerning as many modern devices, including smartphones and smart speakers, are equipped with voice recognition technology. By injecting commands surreptitiously, attackers can potentially trigger actions such as initiating unauthorized transactions, compromising privacy, or even controlling connected smart home devices.
3. Overloading Devices and Frying Circuits
In addition to injecting voice commands, VoltSchemer attacks can also involve overloading devices with excessive voltage, leading to hardware damage. By manipulating the charging process, attackers can send surges of electricity to the device, overwhelming its circuits and causing irreparable damage. This not only renders the device unusable but can also pose safety risks, such as the potential for fires or electrical hazards.
Countermeasures Against VoltSchemer Attacks
To mitigate the risks posed by VoltSchemer attacks, it is essential to implement robust countermeasures at both the hardware and software levels.
Here are some effective strategies for defending against these attacks:
1. Firmware and Protocol Hardening
Device manufacturers should regularly update firmware to patch known vulnerabilities and strengthen wireless charging protocols. By implementing robust encryption, authentication mechanisms, and error-checking protocols, manufacturers can make it more difficult for attackers to exploit weaknesses in the charging process.
2. Secure Voice Recognition Systems
To prevent malicious voice commands from being executed, device manufacturers should enhance the security of their voice recognition systems. This includes implementing multi-factor authentication, voice biometrics, and anomaly detection algorithms to differentiate between legitimate and malicious commands.
3. Voltage Regulation and Surge Protection
Devices should be equipped with voltage regulation mechanisms and surge protection circuits to prevent damage from electrical surges. By monitoring voltage levels and automatically shutting down in the event of a surge, devices can mitigate the risk of hardware damage caused by VoltSchemer attacks.
4. User Awareness and Education
End-users should be educated about the risks of VoltSchemer attacks and encouraged to take proactive measures to protect their devices. This includes avoiding untrusted charging pads, regularly updating device firmware, and being vigilant for signs of suspicious activity, such as unexpected voice commands or device malfunctions.
5. Security Audits and Testing
Device manufacturers should conduct regular security audits and penetration testing to identify and address potential vulnerabilities proactively. By simulating VoltSchemer attacks in controlled environments, manufacturers can assess the effectiveness of their countermeasures and make necessary adjustments to enhance security.
Conclusion
VoltSchemer attacks represent a significant threat to the security and integrity of wireless charging technology. By understanding the modus operandi of these attacks and implementing effective countermeasures, device manufacturers and end-users can mitigate the risks and safeguard against potential exploitation.
Through a combination of firmware hardening, secure voice recognition systems, voltage regulation, user education, and ongoing security testing, we can defend against VoltSchemer attacks and ensure the continued safety and reliability of wireless charging technology.
Read more on https://cybertechworld.co.in for insightful cybersecurity related content.


















This page is incredible. The brilliant information reveals the administrator’s interest. I’m awestruck and envision further such mind blowing material.
Thanks.
This site is incredible. The radiant material shows the administrator’s enthusiasm. I’m dumbfounded and envision more such astonishing substance.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
I think other site proprietors should take this web site as an model, very clean and great user genial style and design, as well as the content. You are an expert in this topic!
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?