
Table of Contents
Introduction
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, organizations face an ever-growing threat of cyber attacks and breaches. To effectively address these risks, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) developed the NIST Cybersecurity Framework. This framework serves as a comprehensive guide to help organizations build a strong foundation for cyber resilience, enabling them to better protect their sensitive information and critical assets.
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework provides a structured approach for organizations to assess and improve their cybersecurity posture. It offers a set of best practices, standards, and guidelines that organizations can adopt to enhance their ability to prevent, detect, respond to, and recover from cyber threats. By following the framework’s principles, organizations can establish robust cybersecurity practices, strengthen their defenses, and minimize the impact of potential cyber incidents.
The significance of the NIST Cybersecurity Framework lies in its ability to address the dynamic nature of cyber threats. It recognizes that a strong cybersecurity strategy is not solely focused on prevention but encompasses a holistic approach to managing risks and building resilience.
By adopting the framework, organizations gain the following benefits:
1. Comprehensive Risk Management: The framework helps organizations identify and understand their unique cybersecurity risks, enabling them to prioritize their resources effectively. It emphasizes the importance of risk assessment, vulnerability management, and the implementation of protective measures to mitigate potential threats.
2. Enhanced Incident Response: The NIST Cybersecurity Framework emphasizes the importance of having a robust incident response plan in place. It guides organizations in establishing clear processes and procedures to promptly detect, respond to, and recover from cybersecurity incidents. This proactive approach minimizes the impact of attacks and ensures a quick return to normal operations.
3. Adaptability to Changing Threat Landscape: The NIST framework acknowledges that cyber threats are constantly evolving. It promotes a continuous improvement mindset, encouraging organizations to regularly assess their cybersecurity posture, update their practices, and stay informed about emerging threats and vulnerabilities. This adaptability enables organizations to stay one step ahead of attackers and effectively manage new risks.
4. Alignment with Industry Best Practices: The NIST Cybersecurity Framework aligns with industry standards, regulations, and best practices, such as ISO 27001 and the CIS Controls. By adopting the framework, organizations demonstrate their commitment to meeting compliance requirements and ensuring that their cybersecurity measures are in line with established industry norms.
5. Collaboration and Information Sharing: The NIST Cybersecurity Framework fosters collaboration between organizations, industry sectors, and government agencies. It encourages the sharing of threat intelligence, best practices, and lessons learned, enabling collective defense and strengthening the overall cybersecurity posture of the community.
Understanding the NIST Cybersecurity Framework
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework is a set of guidelines developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), a U.S. government agency. It was created in response to the increasing cyber threats faced by organizations across various industries. The framework provides a structured approach to help organizations assess, improve, and communicate their cybersecurity posture.
The primary purpose of the NIST Cybersecurity Framework is to help organizations manage and mitigate cybersecurity risks effectively. It offers a flexible and customizable framework that enables organizations to align their cybersecurity practices with their specific business needs, risk tolerance, and available resources. By implementing the framework’s recommendations, organizations can enhance their cybersecurity defenses, reduce the risk of cyber incidents, and improve their overall cyber resilience.
The development of the NIST Cybersecurity Framework involved collaboration between industry experts, government agencies, and private sector organizations. It was first released in 2014 as a result of an executive order issued by the President of the United States to improve critical infrastructure cybersecurity. The framework was developed through extensive research, consultations, and feedback from various stakeholders.
NIST conducted multiple workshops, engaged with industry leaders, and solicited public input to ensure that the framework reflected the diverse needs and perspectives of organizations. The resulting framework is based on industry best practices, existing standards, and lessons learned from real-world cyber incidents. It provides organizations with a common language and methodology to assess and improve their cybersecurity capabilities.
Since its initial release, the NIST Cybersecurity Framework has gained widespread recognition and adoption globally, serving as a valuable resource for organizations of all sizes and sectors. It has been widely acknowledged for its practicality, flexibility, and ability to adapt to evolving cyber threats. The framework continues to evolve, with periodic updates and revisions to ensure its relevance in the face of emerging risks and technologies.
Overall, the NIST Cybersecurity Framework serves as a critical tool for organizations to strengthen their cybersecurity posture, manage risks, and establish a solid foundation for cyber resilience. By following its guidelines, organizations can enhance their ability to protect sensitive information, defend against cyber threats, and maintain the trust and confidence of their stakeholders.
NIST Cybersecurity Framework Categories
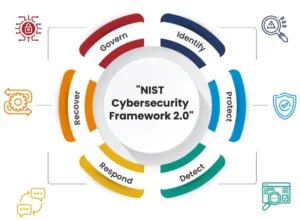
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework is structured into five core functions: Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover. Within each of these core functions, the framework provides categories that offer detailed guidance on specific activities and outcomes. Let’s explore these categories and their significance within each core function:
1. Identify: The Identify function focuses on understanding an organization’s assets, risks, and vulnerabilities. The framework provides the following categories to support this function:
– Asset Management: Helps organizations identify and manage their critical assets, including information, systems, and infrastructure.
– Business Environment: Assists in understanding the organization’s mission, objectives, stakeholders, and the regulatory and legal landscape.
– Governance: Provides guidance on establishing effective cybersecurity governance, including policies, roles, responsibilities, and accountability.
– Risk Assessment: Aids in identifying and assessing cybersecurity risks to determine the potential impact and likelihood of threats.
– Risk Management Strategy: Helps organizations develop and implement a risk management strategy aligned with their objectives and risk tolerance.
2. Protect: The Protect function focuses on implementing safeguards to protect an organization’s assets and minimize the impact of cyber threats. The framework offers the following categories:
– Access Control: Guides the implementation of access controls and user authentication mechanisms to ensure authorized access to resources.
– Awareness and Training: Supports the development of cybersecurity awareness programs and training for employees, promoting a security-conscious culture.
– Data Security: Provides guidance on protecting data through encryption, data handling procedures, and secure data storage.
– Information Protection Processes and Procedures: Helps establish and maintain processes for data backup, data retention, and secure disposal of information.
– Protective Technology: Assists in selecting, implementing, and managing cybersecurity technologies and solutions to protect against threats.
3. Detect: The Detect function focuses on identifying cybersecurity events promptly. The framework includes the following categories:
– Anomalies and Events: Provides guidance on establishing mechanisms to detect anomalies, incidents, and potential cybersecurity events.
– Continuous Monitoring: Aids in the implementation of continuous monitoring processes to detect and respond to security incidents in real-time.
– Detection Processes: Helps organizations develop and implement processes for timely detection of cybersecurity events through monitoring, analysis, and reporting.
4. Respond: The Respond function mainly focuses on responding to detected cybersecurity incidents effectively. The framework offers the following categories:
– Response Planning: Guides the development of an incident response plan that outlines roles, responsibilities, and communication channels during incidents.
– Communications: Assists in establishing effective communication channels to facilitate the reporting, coordination, and escalation of cybersecurity incidents.
– Analysis: Helps organizations conduct forensic analysis, investigate incidents, and determine the root causes to prevent future occurrences.
– Mitigation: Provides guidance on implementing appropriate actions to contain and mitigate the impact of cybersecurity incidents.
– Improvements: Supports organizations in incorporating lessons learned from incidents into their response plans and improving their incident response capabilities.
5. Recover: The Recover function focuses on restoring services and operations after a cybersecurity incident. The framework includes the following categories:
– Recovery Planning: Guides the development of recovery plans and processes to restore affected systems and assets.
– Improvements: Assists in identifying opportunities to improve the organization’s recovery capabilities based on lessons learned from incidents.
– Communications: Aids in developing communication strategies and channels to notify stakeholders, customers, and partners during the recovery process.
– Recovery Coordination: Provides guidance on coordinating activities and resources to support the timely recovery of systems and services. By leveraging the framework’s categories within each core function, organizations can gain a detailed understanding of the specific activities and outcomes required to enhance their cybersecurity posture. This helps in developing comprehensive cybersecurity strategies, implementing effective controls, and aligning with industry best practices to protect against cyber threats.
NIST Cybersecurity Framework Implementation Tiers
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework introduces four implementation tiers that provide organizations with a means to assess their cybersecurity maturity and their ability to achieve cyber resilience. These tiers help organizations understand where they currently stand in terms of their cybersecurity practices and provide guidance on how to progress towards higher levels of maturity. Let’s explore these implementation tiers and their significance:
Tier 1 – Partial:
In Tier 1, organizations have an ad hoc approach to cybersecurity and lack a formalized strategy. They have limited awareness of their cybersecurity risks and may have basic security measures in place. The significance of Tier 1 is that it serves as a starting point for organizations to begin their cybersecurity journey. It highlights the need for organizations to recognize the importance of cybersecurity and take steps to improve their practices. Organizations at this tier may have a fragmented approach to cybersecurity, and their ability to detect and respond to incidents may be limited.
Tier 2 – Risk Informed:
In Tier 2, organizations have a more defined and risk-informed approach to cybersecurity. They have a better understanding of their cybersecurity risks and have implemented policies and procedures to address them. The significance of Tier 2 is that organizations start to establish a more structured approach to cybersecurity. They conduct risk assessments, develop risk mitigation strategies, and have mechanisms in place to track and manage cybersecurity events. Organizations at this tier are proactive in identifying and managing cybersecurity risks but may still have gaps in their capabilities.
Tier 3 – Repeatable:
In Tier 3, organizations have established a repeatable and consistent approach to cybersecurity. They have formalized processes and procedures in place and actively manage their cybersecurity practices. The significance of Tier 3 is that organizations have achieved a level of consistency and effectiveness in their cybersecurity efforts. They have defined roles and responsibilities, conduct regular risk assessments, and continuously monitor and evaluate their security posture. Organizations at this tier are better equipped to detect and respond to incidents and have a framework for improvement in place.
Tier 4 – Adaptive:
In Tier 4, organizations have an adaptive and dynamic approach to cybersecurity. They have the ability to anticipate and respond to changing threats and have implemented advanced cybersecurity practices. The significance of Tier 4 is that organizations demonstrate a high level of maturity and agility in their cybersecurity capabilities. They actively seek out emerging threats, leverage threat intelligence, and regularly update their cybersecurity practices. Organizations at this tier have a strong cyber resilience posture and continuously evolve their cybersecurity measures to stay ahead of potential threats.
The implementation tiers serve as a roadmap for organizations to assess their current cybersecurity maturity and set goals for improvement. They provide organizations with a framework to understand where they stand and help them determine the necessary steps to enhance their cybersecurity capabilities. By progressing through the tiers, organizations can build a solid foundation for cyber resilience, improve their ability to detect and respond to incidents, and effectively manage cybersecurity risks. It is important to note that the implementation tiers are not meant to be prescriptive or one-size-fits-all.
They are designed to provide organizations with flexibility and allow for customization based on their specific needs, risk tolerance, and available resources. Organizations should aim to progress through the tiers at a pace that aligns with their capabilities and strategic objectives.
Establishing a Cyber Resilience Strategy
In today’s digital landscape, organizations face an ever-increasing threat of cyber attacks and data breaches. It is no longer enough to focus solely on prevention; organizations must also prioritize building cyber resilience to effectively withstand and recover from cyber incidents. Establishing a robust cyber resilience strategy is crucial to ensure the continuity of operations, protect sensitive information, and maintain the trust of stakeholders. Here are key steps to consider when developing a cyber resilience strategy:
1. Risk Assessment:
Begin by conducting a comprehensive risk assessment to identify and understand the potential cyber risks facing your organization. This involves evaluating the likelihood and impact of various threats, assessing vulnerabilities in systems and processes, and understanding the potential consequences of a cyber incident. This step provides a foundation for building a tailored and effective cyber resilience strategy.
2. Define Objectives and Priorities:
Establish clear objectives and priorities for your cyber resilience strategy. Consider factors such as business objectives, industry requirements, legal and regulatory obligations, and the specific risks identified in the risk assessment. Define measurable goals and milestones that align with your organization’s overall strategic vision.
3. Prevention and Protection:
Implement preventive measures to minimize the likelihood of cyber incidents. This includes establishing robust security controls, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, encryption, and secure access controls. Regularly update and patch software and systems, and promote a strong security culture among employees through training and awareness programs. Implementing a defense-in-depth approach ensures that even if one layer of defense fails, others are in place to mitigate the risk.
4. Incident Response Planning:
Develop a robust incident response plan that outlines the steps to be taken in the event of a cyber incident. This includes establishing clear roles and responsibilities, defining communication channels, and identifying key internal and external stakeholders. Conduct regular tabletop exercises and simulations to test the effectiveness of the plan and identify areas for improvement. A well-prepared and practiced incident response plan enables swift and effective response, minimizing the impact of an incident.
5. Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery:
Ensure your organization has robust business continuity and disaster recovery plans in place. These plans outline the steps to be taken to maintain critical business operations during and after a cyber incident. Consider backup and recovery strategies, alternative communication channels, and redundancy measures to ensure essential services can continue even in the face of disruption. Regularly test and update these plans to adapt to evolving threats and organizational changes.
6. Continuous Monitoring and Improvement:
Implement continuous monitoring practices to detect and respond to cyber threats in real-time. Use security information and event management (SIEM) systems, intrusion detection systems, and threat intelligence feeds to proactively identify potential threats. Regularly evaluate and update security controls, processes, and policies based on emerging threats and lessons learned from incidents. Foster a culture of continuous improvement to adapt to the evolving threat landscape.
7. Collaboration and Information Sharing:
Engage in information sharing and collaboration with other organizations, industry groups, and government agencies. Sharing threat intelligence, best practices, and lessons learned enables collective defense and enhances the overall cyber resilience of the community. Participate in industry forums, join Information Sharing and Analysis Centers (ISACs), and establish partnerships to leverage shared knowledge and resources.
8. Training and Awareness:
Invest in ongoing training and awareness programs to educate employees about cybersecurity best practices and the role they play in maintaining cyber resilience. Promote a culture of security awareness, emphasizing the importance of reporting suspicious activities, following security protocols, and practicing good cyber hygiene. Regularly communicate updates on emerging threats and provide practical guidance to empower employees to make informed security decisions.
9. Regular Testing and Review: Periodically test and review your cyber resilience strategy to ensure its effectiveness. Conduct vulnerability assessments, penetration testing, and red team exercises to identify weaknesses and validate security controls.
Implementing the NIST Cybersecurity Framework
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework provides a flexible and comprehensive approach to managing and mitigating cybersecurity risks. Implementing this framework can help organizations improve their cybersecurity posture and enhance their ability to prevent, detect, respond to, and recover from cyber incidents. Here are key steps to consider when implementing the NIST Cybersecurity Framework:
1. Familiarize Yourself with the Framework:
Start by gaining a thorough understanding of the NIST Cybersecurity Framework and its components. Review the framework’s core functions (Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover) and the accompanying categories and subcategories. Familiarize yourself with the framework’s guidelines and implementation guidance provided by NIST.
2. Assess Current Cybersecurity Practices:
Conduct an assessment of your organization’s current cybersecurity practices. Identify existing strengths and weaknesses in each core function and category of the framework. This assessment will serve as a baseline to measure progress as you implement the framework.
3. Set Priorities and Objectives:
Based on the assessment, establish priorities and objectives for implementing the NIST Cybersecurity Framework. Determine which areas require immediate attention and allocate resources accordingly. Set measurable goals to track progress and ensure alignment with the organization’s overall strategic objectives.
4. Develop an Implementation Plan:
Create a comprehensive implementation plan that outlines specific actions and milestones for each core function and category. Define responsible individuals or teams for each action item and establish timelines for completion. Consider the organization’s resources, budget, and risk tolerance when developing the plan.
5. Customize the Framework to Your Organization:
Tailor the framework to meet the specific needs and characteristics of your organization. Customize the subcategories, activities, and outcomes based on your industry, size, regulatory requirements, and risk landscape. This ensures that the framework aligns closely with your organization’s unique cybersecurity challenges.
6. Implement Controls and Practices:
Implement the recommended controls and practices outlined in the framework. This may include activities such as conducting risk assessments, developing policies and procedures, implementing access controls, enhancing employee training and awareness programs, and integrating incident response capabilities. Choose controls that best address your organization’s identified risks and capabilities.
7. Monitor and Measure Progress:
Establish mechanisms to monitor and measure your progress in implementing the framework. Regularly assess the effectiveness of controls, track performance against established goals, and identify areas that require improvement. This monitoring process helps identify emerging risks, measure the impact of implemented controls, and drive continuous improvement.
8. Engage Stakeholders:
Involve relevant stakeholders throughout the implementation process. This includes executive leadership, IT teams, employees, and external partners. Communicate the goals and benefits of implementing the framework, solicit feedback, and encourage collaboration. Engaging stakeholders fosters a culture of shared responsibility and helps ensure successful adoption and integration of the framework.
9. Regularly Review and Update:
Periodically review and update your implementation of the NIST Cybersecurity Framework. Stay informed about emerging threats, evolving best practices, and updates from NIST. Regularly assess and adjust your cybersecurity practices to address new risks and changes in the organizational landscape. By following these steps, organizations can effectively implement the NIST Cybersecurity Framework and improve their overall cybersecurity posture. The framework provides a structured and adaptable approach to managing cybersecurity risks, enabling organizations to enhance their resilience and protect valuable assets from cyber threats.
Integrating Cyber Resilience into the Organizational Culture
Cyber resilience is not solely a technical matter but also a cultural one. To effectively withstand and recover from cyber incidents, organizations must integrate cyber resilience into their organizational culture. This means fostering a mindset that prioritizes cybersecurity, encourages proactive risk management, and empowers all employees to play a role in maintaining a strong security posture. Here are key steps to integrate cyber resilience into the organizational culture:
1. Leadership Commitment:
Leadership commitment is crucial in establishing a cyber resilient culture. Executives and senior management should visibly demonstrate their commitment to cybersecurity by championing its importance, allocating adequate resources, and leading by example. When leaders prioritize cybersecurity, it sends a clear message to employees that protecting the organization’s information and assets is a top priority.
2. Awareness and Training:
Develop a robust cybersecurity awareness and training program for all employees. This program should educate employees about common cyber threats, best practices for safeguarding information, and their role in maintaining cyber resilience. Regularly reinforce training through workshops, simulations, and ongoing communication to ensure that cybersecurity remains at the forefront of employees’ minds.
3. Employee Engagement:
Engage employees at all levels of the organization in cybersecurity efforts. Encourage them to actively participate in identifying and reporting potential risks, such as suspicious emails or unauthorized access attempts. Establish channels for employees to share their cybersecurity concerns and ideas for improvement. Recognize and reward employees who demonstrate good cyber hygiene and contribute to the organization’s cyber resilience.
4. Clear Policies and Procedures:
Develop clear and concise cybersecurity policies and procedures that align with industry best practices and regulatory requirements. Communicate these policies effectively to all employees and ensure they understand their responsibilities in adhering to them. Regularly review and update policies to reflect evolving cyber threats and technological advancements.
5. Embed Security in Processes:
Integrate cybersecurity into the organization’s business processes and decision-making. Incorporate security considerations from the early stages of new projects, systems, and initiatives. This ensures that security is not an afterthought but an integral part of the organization’s operations. Implement secure coding practices, conduct regular vulnerability assessments, and prioritize security in third-party vendor evaluations.
6. Continuous Improvement:
Foster a culture of continuous improvement in cybersecurity. Encourage employees to report security incidents, near misses, and vulnerabilities without fear of retribution. Conduct thorough post-incident reviews to identify lessons learned and implement necessary improvements. Regularly assess and update security controls, staying abreast of emerging threats and best practices.
7. Collaboration and Information Sharing:
Promote collaboration and information sharing both internally and externally. Encourage employees to collaborate on cybersecurity initiatives, share knowledge, and learn from each other’s experiences. Engage with industry peers, participate in information sharing forums, and contribute to the collective defense against cyber threats. Sharing insights and lessons learned strengthens the organization’s overall cyber resilience.
8. Measure and Communicate Success:
Establish metrics to measure the effectiveness of cybersecurity efforts and regularly communicate progress to employees. Provide feedback on the impact of their actions and engagement in maintaining cyber resilience. Highlight success stories and share examples of employees who have contributed to mitigating cyber risks. This reinforces the importance of cybersecurity and motivates employees to remain vigilant. By integrating cyber resilience into the organizational culture, organizations can create an environment where cybersecurity is everyone’s responsibility. It empowers employees to actively contribute to protecting the organization’s information and assets, strengthens the organization’s ability to prevent and respond to cyber incidents, and ultimately builds a resilient and secure organization.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the NIST Cybersecurity Framework serves as a vital tool for organizations looking to establish a strong foundation for cyber resilience. By following its principles and adopting its best practices, organizations can enhance their risk management capabilities, respond effectively to incidents, and adapt to the ever-changing threat landscape. Ultimately, implementing the framework empowers organizations to protect their valuable assets, maintain business continuity, and safeguard their reputation in an increasingly digital world.
Do follow on “https://cybertechworld.co.in” for more such insightful cybersecurity content.


















I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.